Botany is the study of plants and their relationship to the environment and other organisms. One of the most important aspects of botany is understanding the fundamental nutrients and elements required for life. All living organisms require a certain set of elements and nutrients in order to grow and function properly. These elements can be broken down into two categories: macronutrients and micronutrients.
Macronutrients are elements that are required in large quantities, such as carbon (C), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These elements are essential for plant growth, photosynthesis, and energy production.
Carbon is the building block of all living matter, making up approximately 50% of the dry weight of a plant. Carbon is an essential component of plant cells and is the main component of carbohydrates, which are used by the plant for energy storage.
Oxygen is used by the plant for respiration, and is required for the production of energy through cellular respiration. Nitrogen is an essential component of chlorophyll and is required for the production of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Nitrogen is also a component of other organic compounds, such as nucleic acids and enzymes.
Phosphorus is involved in energy transfer and storage, as well as being a component of DNA and RNA. It is also important for root growth and flowering. Potassium is involved in water balance, photosynthesis, and the regulation of enzymes.
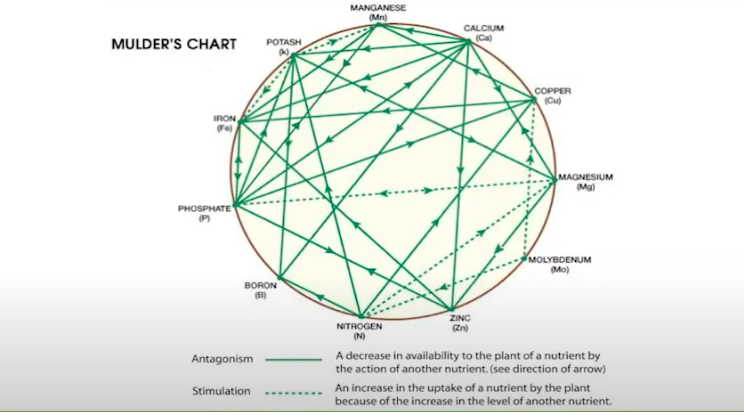
In addition to these macronutrients, plants also require a number of micronutrients, including magnesium (Mg), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), boron (B), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), and molybdenum (Mo). These elements are required in much smaller quantities than the macronutrients, but they are still essential for healthy growth and function.
Magnesium is an essential component of chlorophyll, and is involved in photosynthesis and the activation of enzymes. Iron is involved in the production of chlorophyll and the transportation of electrons in photosynthesis. Manganese is involved in the activation of enzymes, the production of hormones, and the transportation of electrons in photosynthesis.
Boron is involved in cell wall development, root growth, and the production of flowers and seeds. Zinc is involved in the activation of enzymes, the production of hormones, and the transportation of electrons in photosynthesis. Copper is involved in the activation of enzymes and the transportation of electrons in photosynthesis. Molybdenum is involved in the nitrogen metabolism of plants, and is required for the production of nitrates and nitrogen fixation.
Silicon (Si), strictly speaking, is not a necessary element. But it absolutely helps to have it, it stiffens and strengthens cell walls. In animals, it increases bone density.
In order to obtain these essential elements, plants absorb them from the soil through their roots. The form in which the elements are required depends on the type of plant and the environment in which it is growing. Some elements are required in their ionic form, while others are required as organic compounds.
Animals obtain their essential nutrients and elements through their diet, either by eating plants directly or by eating other animals that have consumed plants. The nutrients and elements required by animals are similar to those required by plants, but they are required in different quantities and forms.
In conclusion, the fundamental nutrients and elements required for life are essential for the growth, function, and survival of both plants and animals. Understanding the roles and requirements of these elements is crucial for successful agriculture and animal husbandry, as well as for the understanding of the biology of living organisms.